Blog
Essential Amino Acids: Their Importance to Your Body ?

Protein is the main component of muscles, bones, organs, skin, and nails.
Excluding water, muscles are composed of about 80% protein, making this nutrient especially important for athletes.
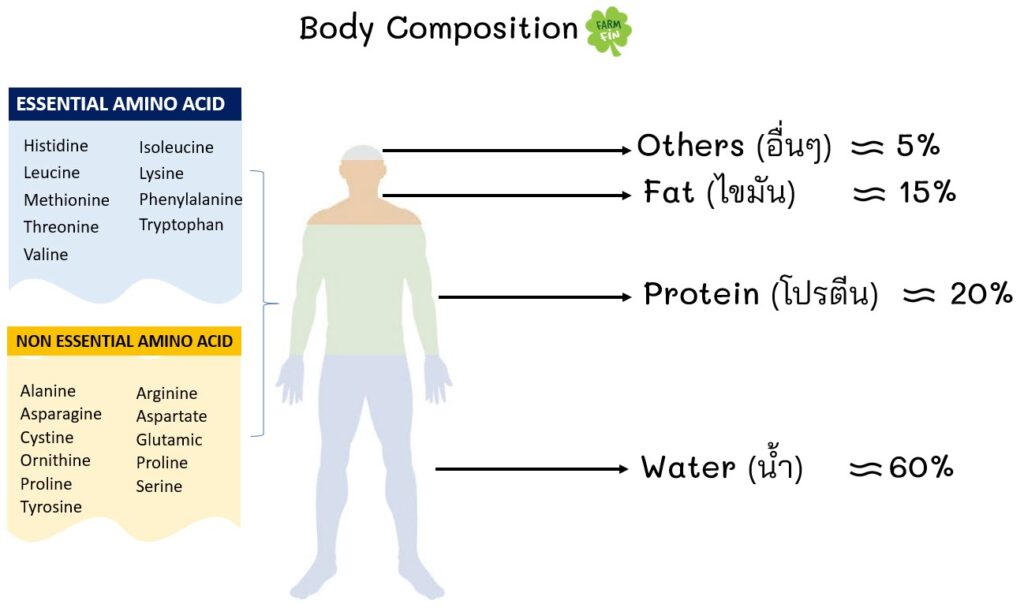
Your body needs 20 different amino acids to grow and function properly. Though all 20 of these are important for your health, only nine amino acids are classified as essential.
These are histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan and valine.
Unlike nonessential amino acids, essential amino acids can’t be made by your body and must be obtained through your diet.
Their Roles in Your Body
The 9 essential amino acids perform a number of important and varied jobs in your body:
Phenylalanine: Phenylalanine is a precursor for the neurotransmitters. It plays an integral role in the structure and function of proteins and enzymes and the production of other amino acids.
Valine: Valine helps stimulate muscle growth and regeneration and is involved in energy production.
Threonine: Threonine is important components of the skin and connective tissue. It also plays a role in fat metabolism and immune function.
Tryptophan: Though often associated with causing drowsiness. It’s a neurotransmitter that regulates your appetite, sleep and mood.
Methionine: Methionine plays an important role in metabolism and detoxification. It’s also necessary for tissue growth and the absorption of zinc and selenium, minerals that are vital to your health.
Leucine: Like valine, leucine is critical for protein synthesis and muscle repair. It also helps regulate blood sugar levels, stimulates wound healing and produces growth hormones.
Isoleucine: The last of the three branched-chain amino acids, isoleucine is involved in muscle metabolism and is heavily concentrated in muscle tissue. It’s also important for immune function, hemoglobin production and energy regulation.
Lysine: Lysine is immune function and the production of collagen and elastin.
Histidine: Histidine is a neurotransmitter that is vital to immune response, digestion, sexual function and sleep-wake cycles.
As you can see, essential amino acids are at the core of many vital processes.
Though amino acids are most recognized for their role in muscle development and repair, the body depends on them for so much more.
That’s why essential amino acid deficiencies can negatively impact your entire body including your nervous, reproductive, immune and digestive systems.
Reference :
– What to know about essential amino acids | Medicine News Today
– Innovation Spotlight: Sacha Inchi | Hammer Nutrition